- Home
- Plate Heat Exchanger
What is a Plate Heat Exchanger and How Does It Work
Heat Transfer Theory
The science of heat transfer is an essential concept in various industries, and its mastery is crucial for optimal performance. At its core, this theory is guided by the principle of equilibrium, where energy flows naturally from high to low temperatures until the balance is achieved.
In the realm of engineering, plate heat exchangers are vital tools that operate based on this principle. By utilizing a plate heat exchanger, heat is effectively isolated, and the hot and cold mediums are separated by a barrier.
As a result, heating and cooling fluids and gases can be efficiently and cost-effectively exchanged with minimal energy consumption.
Understanding the underlying principles of heat transfer is essential for effective problem-solving in thermal engineering. According to this theory:
1) Heat flows from a hot medium to a colder one
2) There must be a temperature difference between the mediums.
3) The heat lost by the hot medium must be equal to the heat gained by the cold medium.
To tackle thermal challenges, the plate heat exchanger calculation method is an effective and proven approach.
By applying this theory and leveraging the efficiency of heat exchangers, industries can achieve optimal performance while minimizing energy consumption.
What is Heat Exchanger
In a simple term, a heat exchanger is a vital component used in various industries to facilitate the transfer of heat between two mediums. This equipment comes in different shapes and sizes, depending on the specific application and thermal requirements.
There are primarily two types of heat exchangers, direct heat exchange and indirect heat exchange. In direct heat exchange, both mediums are in direct contact with each other, resulting in efficient and rapid heat transfer. An example of direct heat exchange is a cooling tower, where the water cools through direct contact with air.
On the other hand, indirect heat exchange involves the use of a barrier or divided media to separate the two mediums. This approach allows for greater control and optimization of the heat transfer process, resulting in enhanced efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
The application of heat exchnager can be found across industrial engineering applications such as refrigeration, airconditioning systems, power plants, food processing systems, chemical processing plant and automobile radiators.
What is the Most Common Heat Exchanger in Industry
The most common heat exchanger in industry is the plate heat exchanger. Plate heat exchangers are essential equipment that plays a critical role in various industrial processes, enabling the efficient and effective transfer of heat between different mediums.
What is a Plate Heat Exchanger
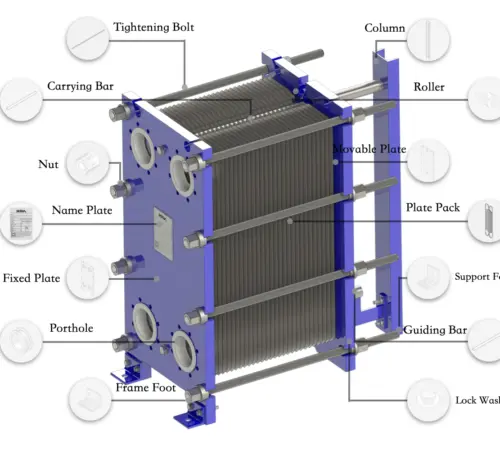
Put simply, a plate heat exchanger (PHE) is a highly efficient device that consists of multiple heat transfer plates held in place by a fixed and a loose pressure plate. The gasket arrangement on each heat transfer plate provides two separate channel systems that enable the primary and secondary media to flow in a counter-current manner without mixing.
This feature, coupled with the corrugated plates that create turbulence in the fluids, results in an effective heat transfer coefficient.
The plate heat exchanger (PHE) design consists of multiple heat transfer plates, secured by a stationary and a movable pressure plate, forming a comprehensive assembly. Each heat transfer plate features a gasket system, which provides two independent channel networks.
The gasket arrangement allows for through-flow in single channels, facilitating counter-current flow of primary and secondary media while preventing their mixing due to the gasket design.
The turbulence caused by corrugated plates as fluids course through the assembly increases the effective heat transfer coefficient, enabling efficient thermal exchange. HFM has an extensive range of plate heat exchangers designed for various industries and applications, catering to heating, cooling, heat recovery, condensation, and evaporation.
How Does a Plate Heat Exchanger Work
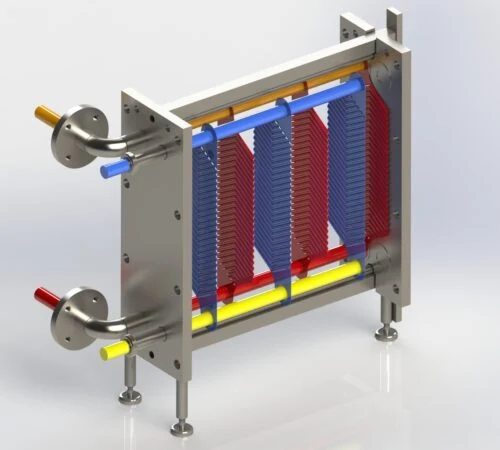
Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers (GPHEs) are designed to optimize heat transfer between two fluids or gases. The corrugated plates within the Gasketed Plate Heat Exchanger allow for efficient heat transfer from one medium to the other.
The plates used in Gasketed Plate Heat Exchanger are equipped with elastomeric gaskets that seal the channels and direct the mediums into alternating channels. The plate pack is placed between a frame plate and a pressure plate and compressed using bolts between the plates.
An upper carrying bar supports the channel and pressure plate, which are then fixed in position by a lower guiding bar on the support column. This design facilitates easy cleaning and modification by adding or removing plates.
4 Main Types of Plate Heat Exchanger
When it comes to plate heat exchangers, there are four primary types optimized for efficient heat transfer across various industrial applications. These versatile devices play a crucial role in optimizing heating and cooling processes.
1. Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers:
Gasketed plate heat exchangers, known for their reliable sealing, are designed to facilitate effective heat exchange. They employ high-quality gaskets to ensure a secure seal, preventing any potential heat loss or leakage. The flexibility of these exchangers makes them ideal for applications requiring precise temperature control and efficient heat transfer.
2. Brazed Plate Heat Exchangers:
In demanding industrial environments, brazed plate heat exchangers excel in delivering high heat transfer rates. Their compact design and efficient heat exchange capabilities make them a cost-effective solution for heating and cooling processes. When constructed with stainless steel plates and copper brazing, these exchangers exhibit exceptional resistance to corrosion, ensuring longevity and reliability.
3. Welded Plate Heat Exchangers:
Designed for heavy-duty applications involving high temperatures and corrosive substances, welded plate heat exchangers provide robust and durable heat exchange solutions. The welding of plates creates a secure and leak-proof configuration, making them suitable for critical processes that demand reliable and efficient heat transfer.
4. Semi-Welded Plate Heat Exchangers:
Combining the advantages of both welded and gasketed plates, semi-welded plate heat exchangers are engineered to balance efficiency and serviceability. These exchangers feature pairs of plates that are both welded and gasketed, offering an optimal solution for applications requiring precise control over heat transfer and temperature regulation.
Unsure about which Plate Heat Exchanger to utilize?
Contact us for 1-on-1 Expert guidance and custom plate heat exchanger design services tailored specifically to your needs!
Advantages of a Plate Heat Exchanger
The Gasketed Plate Heat Exchanger (GPHE) has several advantages:
1) Exceptional heat transfer precision – Improved temperature approach, true counter-current flow, and significantly less hold-up volume (up to 80-90% less).
2) Economically sound choice – Low capital investment, installation costs, and limited maintenance and operating costs.
3) Highly reliable with minimal fouling, stress, wear, and corrosion – A responsible choice with the least energy consumption for maximum process efficiency and reduced cleaning needs.
4) Easily scalable – Allows the expansion of capacity through the adjustment of plates on existing frames, compared to plate and shell heat exchanger.
Disadvantages of a Plate Heat Exchanger
The Gasketed Plate Heat Exchanger (GPHE) has several limitations:
1) Poor sealing could lead to leakage — Entail the inconvenience of replacing the unit
2) Limited pressure tolerance — Typically not exceeding 1.5 MPa
3) Limited operational temperature range — Determined by the gasket material’s temperature resistance.
4) Higher flow resistance — Compared to shell and tube heat exchangers.
HFM Plate Heat Exchanger
In any application concerning fluid heating and cooling, the idea of getting the maximum energy efficiency and reliable performance comes down to the ideal technology and suitable choice for your specific conditions. Over the years, HFM has been developing plate heat exchanger technology and products customized and specific applications to our clients’ variant requirements.
We now offer industrial users the most comprehensive plate heat exchanger options to satisfy the widest range of needs, either complete unit or replacement spare parts. With the experience we and our global partners have gained from the practical project solutions, we can deliver the optimal engineering consult, service, and product support package to you.
Quality Assurance
HFM PHE™ provides plate heat exchangers that adhere to international standards for all industrial clients. Our products meet the requirements of ISO management, Marine & Offshore classification, as well as Euro and American standards. Our products also meet the rigorous requirements of GRG, FDA, and SGS certifications.
HFM Plate Heat Exchanger Portfolio
Find out more HFM solutions for our clients
HFM, along with our global distributors, provide support to customers in various industries for their plate heat exchanger processing requirements. Our tailored design solutions and high-quality product offerings ensure reliable performance for our customers.
Are you looking for cost-saving PHE replacement spare parts?
HFM supplies non-OEM plate heat exchanger spare parts that are fully compatible with PHEs of all brands.
Want to know more? Explore now about our Industry Applications on HFM Youtube Channel.